Description
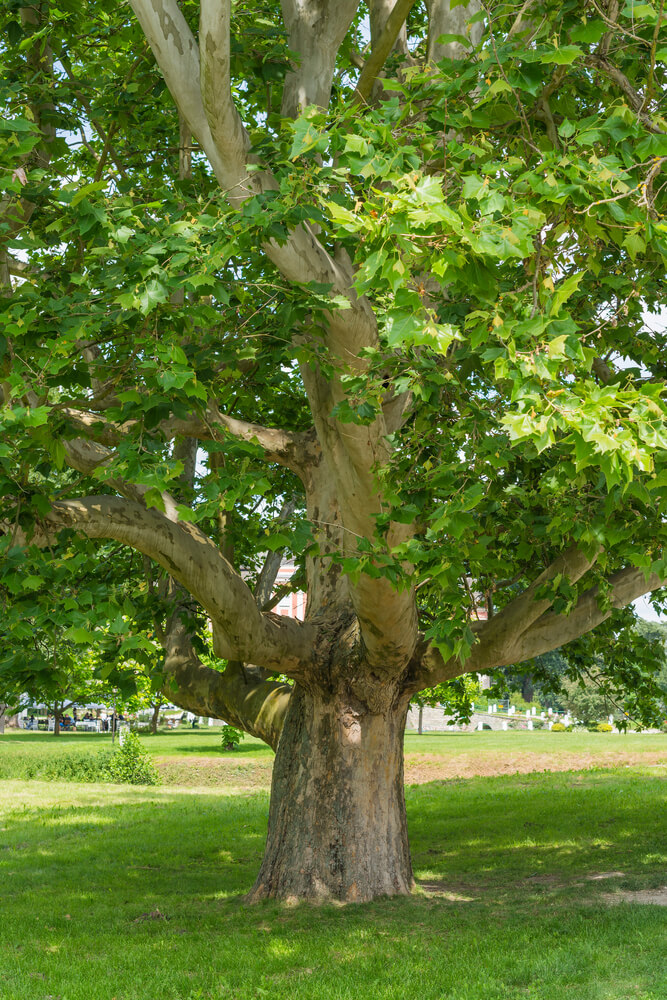
The genus Platanus consists of several species of deciduous trees that are native to North America, Europe, and Asia. These trees are known for their attractive bark, large size, and tolerance to a wide range of growing conditions. Here are some horticultural notes on the genus Platanus:
Climate and soil requirements: Platanus trees are adaptable and can grow in a wide range of climates and soil types. They prefer well-draining soil and can tolerate both wet and dry conditions.
Light requirements: Platanus trees prefer full sun to partial shade.
Watering: Platanus trees require moderate watering, particularly during the growing season. However, they are also drought-tolerant and can survive periods of drought.
Fertilization: Platanus trees benefit from regular fertilization during the growing season, with a balanced fertilizer that is high in nitrogen.
Pruning: Platanus trees require regular pruning to maintain their shape and size. Dead or damaged branches should be removed as soon as possible. Pruning should be done in late winter or early spring, before new growth appears.
Propagation: Platanus trees can be propagated by seed or by rooting stem cuttings. Propagation by seed is the most common method.
Pests and diseases: Platanus trees are relatively pest and disease resistant but may occasionally be affected by fungal diseases such as anthracnose or insect pests such as borers. Regular inspection and treatment can help prevent and control these issues.
Uses: Platanus trees are primarily cultivated for their ornamental value, particularly for their attractive bark and large size. They are often used in landscaping as shade trees, specimen trees, or street trees. Additionally, some Platanus species are used in traditional medicine to treat a variety of ailments.