Description
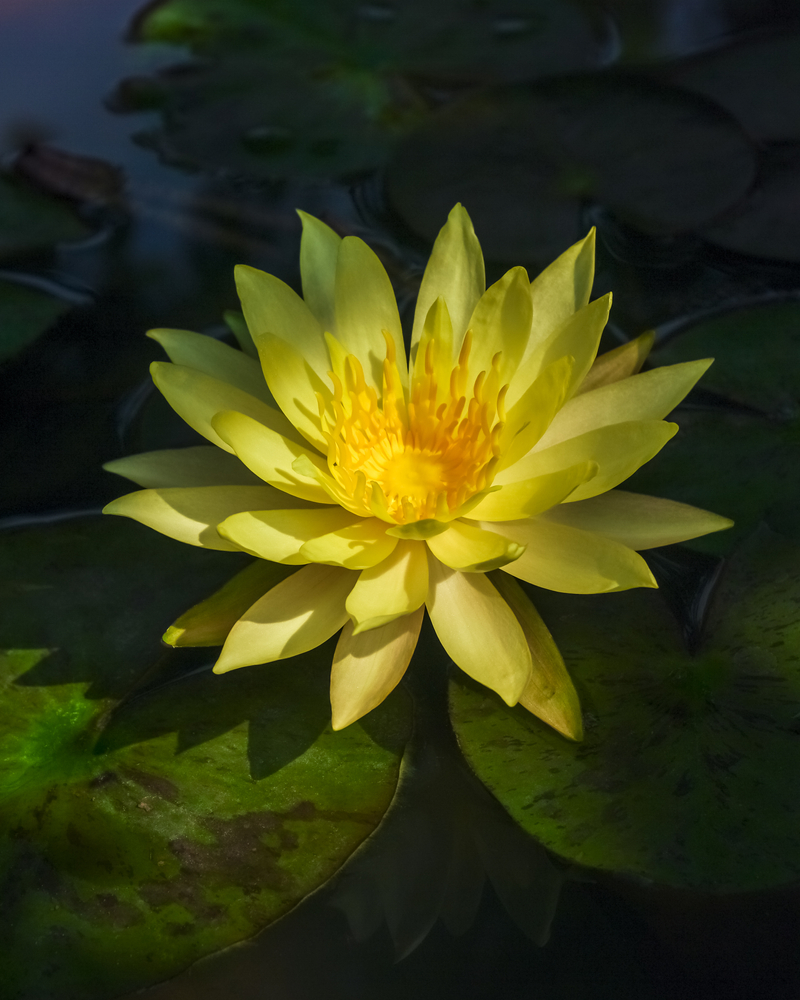
Nymphaea is a genus of aquatic plants in the family Nymphaeaceae. Commonly known as water lilies, Nymphaea species are renowned for their exquisite flowers and floating leaves. They are native to various regions around the world and are highly valued for their beauty and their ability to enhance the aesthetics of water gardens and ponds.
Climate: Nymphaea species thrive in temperate to tropical climates. They require warm temperatures and ample sunlight to grow and bloom successfully. Some species can tolerate colder climates, while others prefer warmer conditions. Choose species suitable for your specific climate and provide protection in extreme heat or cold.
Watering: Nymphaea plants are aquatic and require water to grow. They thrive in still or slow-moving water, such as ponds or water features. Ensure that the water level is consistently high enough to cover the base of the plants. Avoid allowing the water to completely dry out, as it can be detrimental to their growth.
Soil Type: Nymphaea plants do not grow in soil but instead root in the mud or substrate at the bottom of ponds or water bodies. The substrate should be rich in organic matter to provide nutrients for the plants. It should also have good water retention capacity while still allowing water to circulate around the roots.
Fertilizing: Nymphaea plants benefit from regular fertilization to promote healthy growth and vibrant blooms. Use specially formulated aquatic plant fertilizers to provide essential nutrients. Follow the package instructions for the recommended dosage and frequency. Apply the fertilizer to the water or incorporate it into the substrate according to the product guidelines.
Pest & Diseases: Nymphaea plants are generally resistant to pests and diseases. However, they can occasionally be affected by aphids, slugs, or fungal diseases. Monitor the plants regularly for any signs of infestation or disease. Physical barriers or organic pest control methods can be employed. Maintain good water circulation to prevent stagnant conditions.
Pruning: Nymphaea plants require minimal pruning. Remove any yellowing or damaged leaves to maintain the plant’s appearance. Prune off spent flowers to prevent seed formation and encourage continuous blooming. If the plants become too crowded, thin out the growth by removing excess shoots. Avoid heavy pruning, as it can weaken the plants.
Propagation: Nymphaea plants can be propagated through division or by collecting and sowing seeds. Division is typically done in early spring when the plants are actively growing. Carefully separate the rhizomes and replant them in containers or other suitable locations. Seeds can be collected from mature seed pods and sown in a growing medium.
Landscape Uses: Nymphaea plants are ideal for water gardens, ponds, or other aquatic settings. They provide beauty, elegance, and a serene ambiance to these landscapes. Nymphaea species are often used as focal points or as part of larger aquatic plant displays. Their floating leaves and vibrant flowers create a stunning visual impact.
Cultivars: There are numerous cultivated varieties of Nymphaea available, offering variations in flower color, size, and leaf shape. Some popular cultivars include Nymphaea ‘Marliacea Chromatella’ with yellow flowers, Nymphaea ‘Attraction’ with deep red flowers, and Nymphaea ‘Perry’s Baby Red’ with small, compact red flowers. These cultivars provide options for different design preferences and can enhance the beauty and diversity of water gardens and ponds.