Description
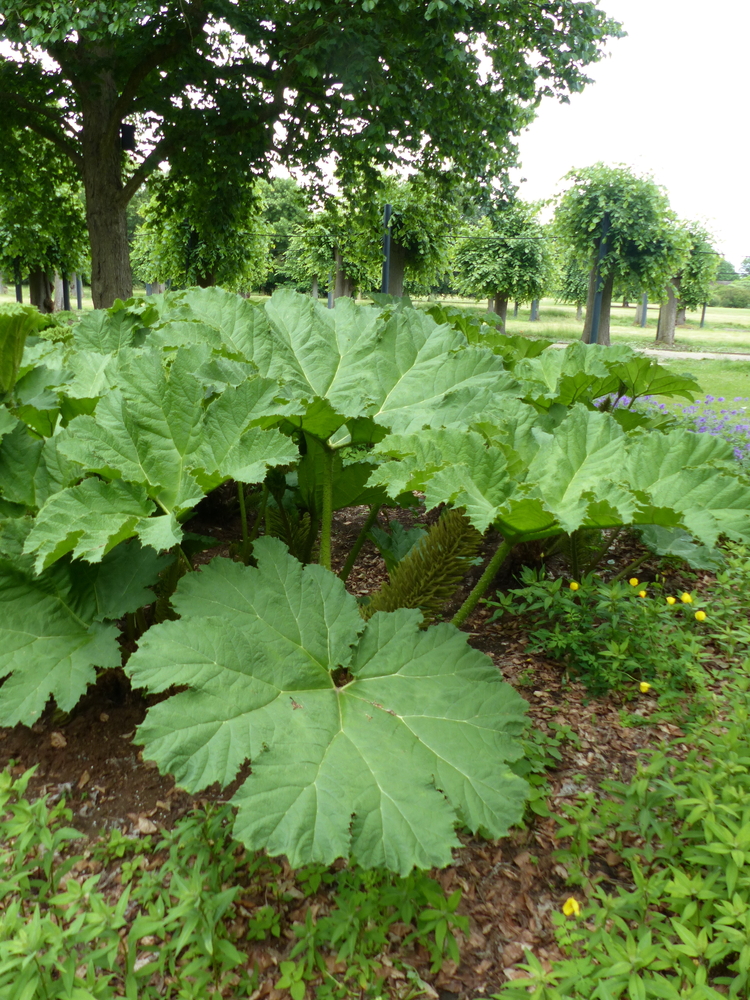
Gunnera is a genus of large-leaved herbaceous plants that are native to damp and boggy areas in South America, New Zealand, and eastern Australia. These plants are commonly known as “giant rhubarb” due to their large, umbrella-like leaves that can reach up to 2 meters in diameter.
Here are some horticultural notes on the genus Gunnera:
Growing conditions: Gunnera plants prefer damp, boggy soil that is rich in organic matter. They are not well-suited to dry or arid conditions. They grow best in partial shade, although they can tolerate full sun in cool, damp climates. In hotter climates, they may require more shade and moisture to thrive.
Watering: These plants require a lot of water and should be kept consistently moist, but not waterlogged. In dry conditions, they may need to be watered daily to prevent wilting.
Fertilizer: Gunnera plants are heavy feeders and require regular fertilization to maintain healthy growth. Use a balanced, all-purpose fertilizer every 2-3 weeks during the growing season.
Pruning: Gunnera plants can grow quite large, and their leaves may begin to flop over or become damaged. Prune back any damaged leaves to the base of the stem, and cut back the entire plant in late fall or early winter to promote new growth in the spring.
Propagation: Gunnera plants can be propagated from seed or by dividing mature plants. Seeds can be sown in the spring or fall, and mature plants can be divided in the spring or early summer.
Pests and diseases: Gunnera plants are generally resistant to pests and diseases, but they may be susceptible to fungal leaf spots and root rot if the soil is too wet. Watch for signs of leaf discoloration or wilting, and adjust watering or drainage as needed.
Uses: Gunnera plants are commonly grown as ornamental specimens in wetland or bog gardens. They can also be used for erosion control, as their large leaves and extensive root systems can help stabilize soil along streambanks or other wetland areas. In some cultures, the stems and rhizomes of Gunnera plants are used for medicinal purposes.