Description
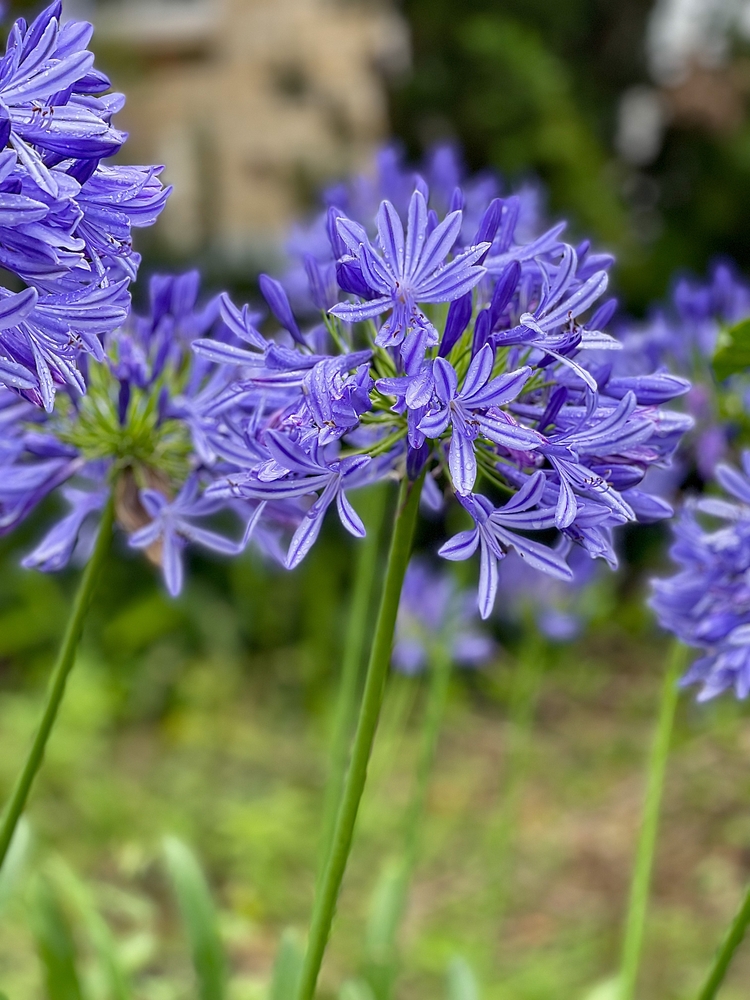
Agapanthus is a genus of perennial flowering plants in the family Amaryllidaceae, commonly known as Lily of the Nile or African lily. These plants are native to South Africa and are grown for their attractive flowers and foliage. Here are some horticultural notes on the genus Agapanthus:
Growing conditions: Agapanthus plants prefer well-draining soil and full sun to partial shade. They are adapted to dry, rocky habitats and are well-suited to rock gardens or xeriscapes.
Propagation: Agapanthus plants can be propagated by seed or by division. Seeds should be sown in the fall or early spring, while division can be done in the spring or fall.
Pruning: Agapanthus plants do not require regular pruning but can be deadheaded after flowering to prevent self-seeding and to encourage additional blooms. The leaves can be cut back in the fall after they turn yellow.
Watering: Agapanthus plants prefer moderate watering and should be watered deeply and infrequently. They can tolerate drought conditions, but may suffer from root rot if over-watered.
Fertilization: Agapanthus plants can benefit from a light application of a balanced fertilizer in the spring and summer.
Pests and diseases: Agapanthus plants are generally resistant to pests and diseases but can be susceptible to snails and slugs. They may also develop fungal diseases if over-watered.
Uses: Agapanthus plants are often used in mixed borders, containers, or mass plantings. They are also well-suited to coastal gardens and can tolerate salt spray and windy conditions.
Varieties: There are several different species and cultivars of Agapanthus, including Agapanthus africanus and Agapanthus praecox. Some varieties have blue or white flowers, while others have variegated foliage. It is important to choose a variety that is well-suited to your growing conditions and desired use.