Description
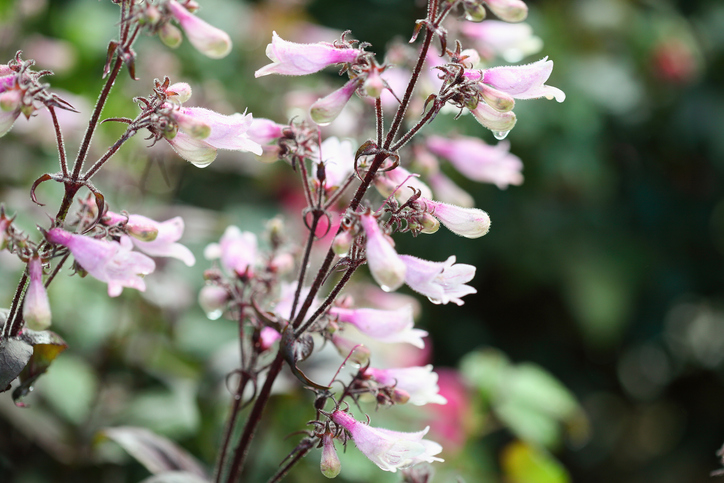
Penstemon is a genus of herbaceous flowering plants in the family Plantaginaceae. Commonly known as beardtongues, Penstemon species are valued for their showy, tubular flowers and attractive foliage. They are native to North America and are widely cultivated for their vibrant blooms and ability to attract pollinators.
Climate: Penstemon plants are adaptable and can be found in a wide range of climates. Different species have varying climate preferences, but most Penstemon species thrive in regions with mild to moderate temperatures. They are well-suited for temperate, Mediterranean, and semi-arid climates.
Watering: Penstemon plants have moderate water needs. They prefer regular watering to keep the soil evenly moist but can tolerate some drought once established. It is important to avoid overwatering, as excessive moisture can lead to root rot. Allow the soil to dry slightly between waterings.
Soil Type: Penstemon plants prefer well-draining soil. They can tolerate a range of soil types, including sandy, loamy, or clay soils. However, they perform best in fertile soil with good organic content. Ensure that the soil has adequate drainage to prevent waterlogging.
Fertilizing: Penstemon plants generally do not require heavy fertilization. Incorporating organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, into the soil during planting provides essential nutrients. An application of a balanced slow-release fertilizer in spring can help promote healthy growth.
Pest & Diseases: Penstemon plants are generally resistant to pests and diseases. However, they may occasionally face issues such as aphids, leafhoppers, or powdery mildew. Regular inspection and appropriate pest control measures can help manage these issues. Ensuring good air circulation around the plants can also prevent fungal diseases.
Pruning: Penstemon plants do not require extensive pruning. However, to maintain their neat appearance and encourage additional blooming, remove spent flower stalks and trim back any straggly growth. Pruning can be done after the main flowering period or in early spring before new growth emerges.
Propagation: Penstemon plants can be propagated through seeds, division, or stem cuttings. Collect seeds from ripe capsules and sow them in containers or directly in the garden. Division can be done in spring or autumn. Stem cuttings can be taken in late spring or early summer and rooted in a well-draining medium.
Landscape Uses: Penstemon plants have versatile landscape uses. They are often used in borders, rock gardens, or as mass plantings to create vibrant displays of colour. Their tall flower spikes and attractive foliage make them suitable for mixed perennial beds or as focal points in the garden. They also attract hummingbirds and butterflies.
Cultivars: ‘Husker Red’, ‘Sour Grapes’, ‘Midnight’, ‘Firebird’, ‘Dark Towers’, ‘Garnet’