Description
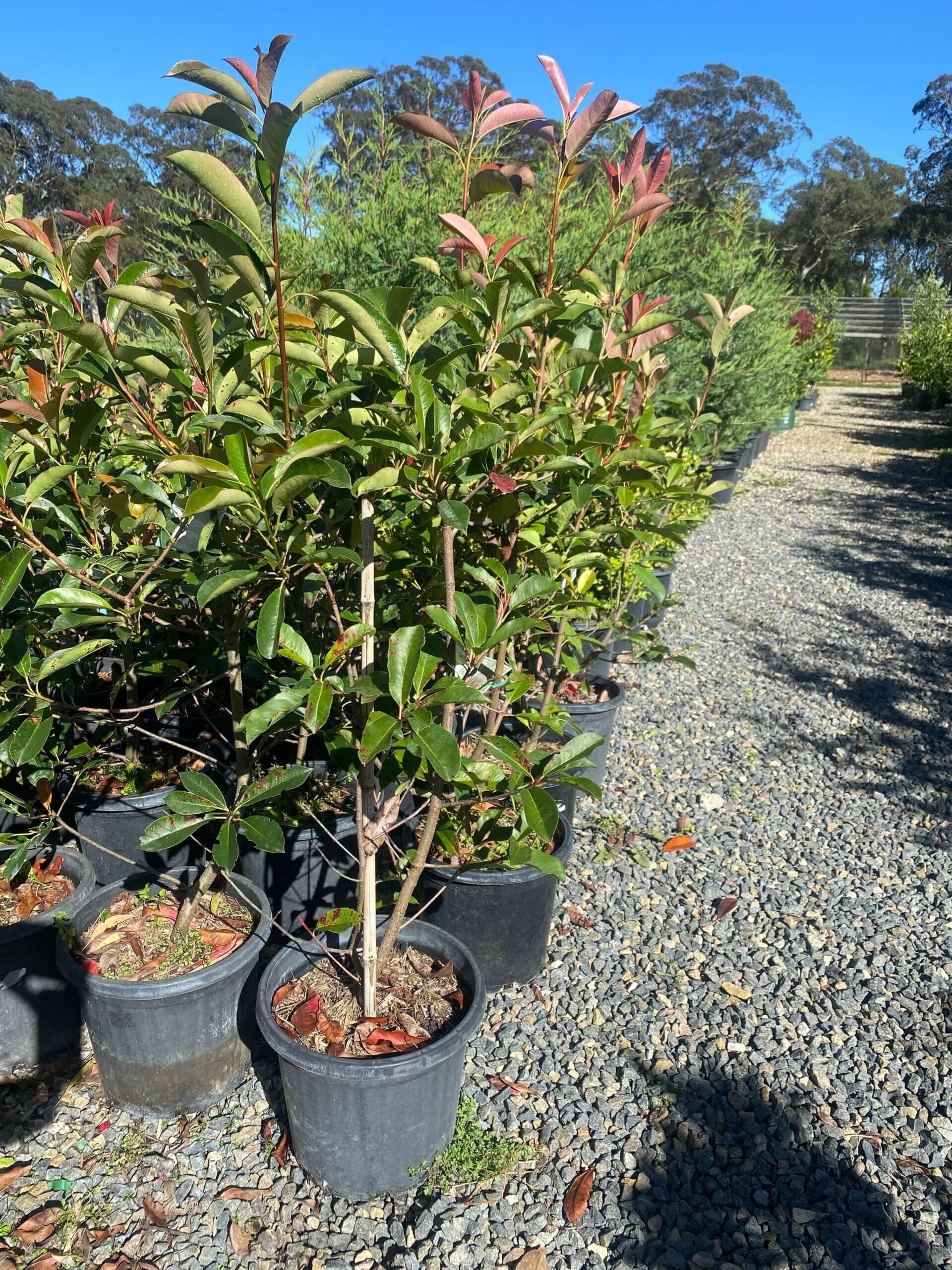
Photinia is a genus of evergreen and deciduous shrubs and trees in the family Rosaceae. Known for their vibrant red new foliage and attractive berries, Photinia species are commonly used for ornamental purposes, hedges, and screening. They have a diverse range of species, some native to Asia and others cultivated for their ornamental features.
Climate: Photinia species thrive in temperate to subtropical climates. They prefer regions with mild winters and warm summers. Some species are more cold-hardy than others. Select species suitable for your specific climate to ensure successful growth.
Watering: Photinia plants have moderate water needs. Water young plants regularly to establish a strong root system. Once established, they are relatively drought-tolerant and require less frequent watering. However, they appreciate consistent moisture during dry spells.
Soil Type: Photinia plants prefer well-draining soil with a slightly acidic to neutral pH. They can tolerate a range of soil types, including loamy or sandy soil. Good drainage is important to prevent waterlogged roots.
Fertilizing: Photinia plants benefit from regular fertilization to support growth and vibrant foliage. Apply a balanced, slow-release fertilizer in early spring. Avoid excessive fertilization, as it can lead to excessive growth at the expense of leaf color.
Pest & Diseases: Photinia plants can be susceptible to some pests and diseases. They are sometimes affected by leaf spot diseases, aphid infestations, and powdery mildew. Regular monitoring and proper sanitation practices can help prevent these issues. Good air circulation and avoiding overhead watering can prevent fungal diseases.
Pruning: Photinia plants require occasional pruning to maintain their shape and encourage new growth. Prune in late winter or early spring when the plant is dormant. Trim back any dead or diseased branches and shape the plant as desired.
Propagation: Photinia plants can be propagated through seeds, cuttings, or layering. Seeds can be collected from mature berries and sown in containers in spring. Semi-hardwood cuttings can be taken in summer and rooted in a well-draining medium. Some species can also be propagated by air layering.
Landscape Uses: Photinia plants are versatile and suitable for various landscape settings. They can be used as standalone specimen plants, in hedges, or as foundation plantings. Their colorful new foliage adds visual interest, and some species produce berries that attract birds.
Cultivars: There are several cultivated varieties of Photinia available, offering variations in growth habit, foliage color, and size. Some popular cultivars include Photinia x fraseri ‘Red Robin’ with bright red new foliage, Photinia serratifolia ‘Pink Crispy’ with pink-edged leaves, and Photinia serrulata ‘Bewley’s Red’ with deep red foliage. These cultivars provide options for different design preferences and can enhance the visual appeal of your garden.