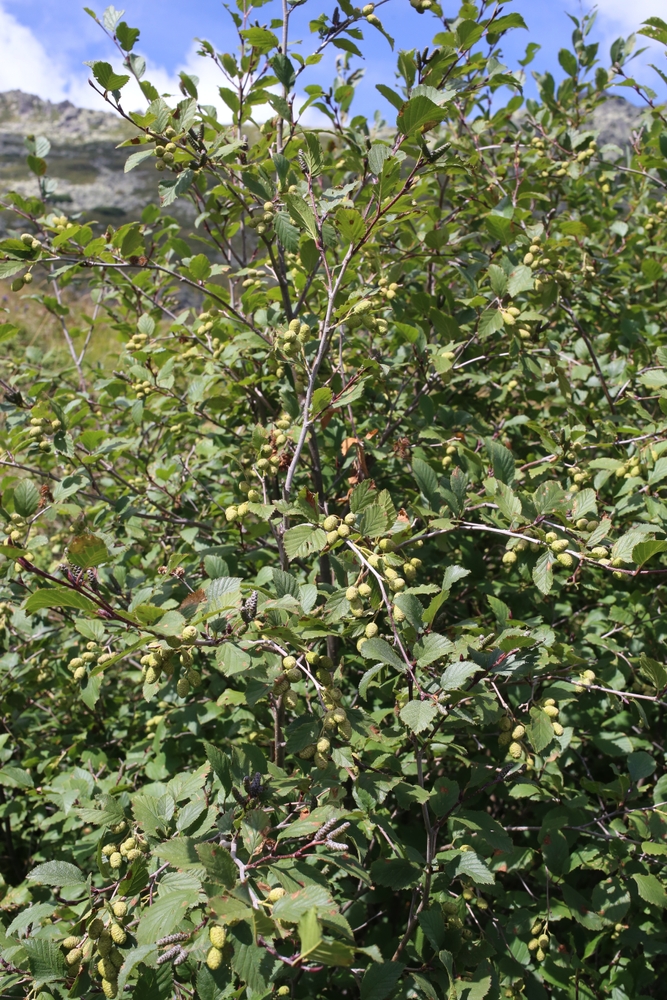
Alnus jorullensis 400mm pot size TREE EVERGREEN
Alnus is a genus of trees and shrubs commonly known as alder. They are native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. Here are some horticultural notes on the genus Alnus:
Growing conditions: Alnus species prefer moist soils and humid climates. They grow well in full sun to partial shade and well-drained soil. They can tolerate periodic periods of wetness and flooding.
Propagation: Alnus can be propagated from seed or by cuttings. Seeds should be sown in the fall, and will require stratification (cold treatment) before germination. Cuttings can be taken in the summer and rooted in a well-draining soil mix.
Watering: Alnus should be watered deeply and frequently. They are adapted to moist conditions and can tolerate periodic periods of wetness.
Fertilizer: Alnus trees benefit from regular fertilization with a balanced fertilizer. Fertilizer should be applied in the spring and fall.
Pruning: Prune Alnus trees and shrubs in the late winter or early spring, before new growth begins. Remove any dead, diseased, or crossing branches. Thin out the center of the tree to promote air circulation.
Pests and diseases: Alnus trees and shrubs are relatively disease-free. However, they may be susceptible to aphids and leaf spot. Regular monitoring and treatment with insecticides or fungicides may be necessary.
Uses: Alnus species are often used for ornamental purposes, such as in landscaping or as shade trees. They are also used for erosion control and to stabilize riverbanks. The wood of some species is used for furniture, cabinetry, and other woodworking purposes. Some species are also used for their medicinal properties.
Description
- Family Name: Betulaceae
- Origin: South America
- Characteristics:
- Foliage Colours: Green
- Flower Colours: Insignificant
- Flower Fragrant: No
- Flowering Season: N/A
- Fruit: No
- Landscape Use(s): Borders / Shrubbery, Cottage Garden,
Formal Garden, Hedging / Screening, Wind Break
- Pest & Diseases: Aphids, Possums
- Plant Care: Keep Moist During Dry Periods, Mulch Well
- Requirements:
- Growth Rate: Fast
- Maintenance Level: Low
- Water Usage: High
- Tolerances:
- Drought: Low
- Frost: High
- Wind: Moderate
- Cultural Notes: Avoid planting to close to homes, paving as these roots can be invasive. Best position large gardens and park land or in
flooded areas on farm land where they can be used a great shade tree.